

Decommissioning
The offshore infrastructure must be removed at the end of its life. Some parts, e.g. the steel tower, can be recycled. However, others, e.g. blades, currently cannot be recycled (or it is too expensive to recycle).

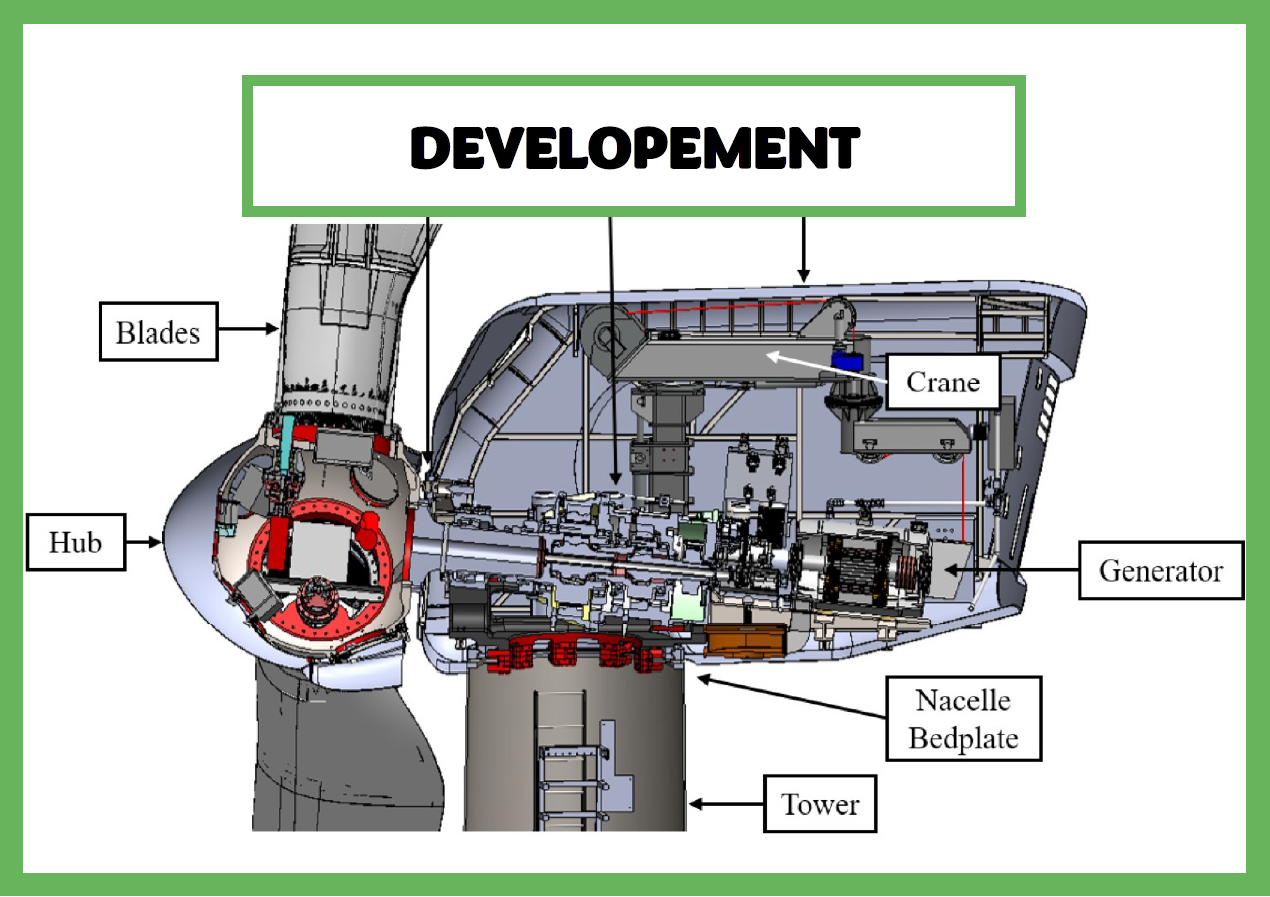
Development
This is a large amount of upfront work including environmental studies, collaboration with the broader community, and design of the turbines.
Installation & commissioning
Both land (e.g. onshore substations) and sea activities (e.g. turbine foundations) are included, the process can take approximately 3 years.

Life extension
The operational life of wind farms can be extended through risk assessments and inspections, it includes addressing regulatory aspects and replacement of wind turbine components.

Manufacturing
This is when all the parts of the wind farm are made. It includes making wind turbine’s rotor, blades, nacelle, and foundation, but also ancillary parts such as cables and substations.

Operations and maintenance
This stage is all about optimising electricity generation. It is important to maximise safe operation of the turbines whilst also maintaining them and the balance of plant.

Re-powering
Old turbines are replaced with more powerful and efficient turbines that use modern technology. The electricity output of new turbines almost doubles!

For an informal discussion, call +44 (0) 1482 463331
or contact auracdt@hull.ac.uk